If you’ve ever done a Reddit search for “best next-generation firewall,” Palo Alto Networks has likely been on the list. Many companies choose Palo Alto firewalls because they offer innovative next-generation firewall (NGFW) capabilities for everything from AWS to Google to Microsoft. However, these powerful firewalls can often be complicated to deploy and maintain.
Whether just getting started on your journey or looking to double check your work, this Palo Alto firewall checklist gives you some suggestions to help you optimize your deployment. As your environment grows and becomes more complex, maintaining these Palo Alto best practices may feel overwhelming. With Tufin, you can standardize firewall rules and simplify firewall management to improve security and business agility.
Decrypt Traffic
While seemingly counterintuitive, Palo Alto firewall best practices start with decryption so that you can identify applications. When setting up decryption:
- Decrypt traffic that is not private or sensitive as possible
- Review compliance requirements before implementing decryption
- Prioritize traffic to decrypt by focusing on allowed devices, sanctioned applications, and user group needs
- Identify traffic that you can’t decrypt
- Deploy SSL decryption best practices, including SSL forward proxy and inbound inspection profiles
- Configure decryption logging and log forwarding
Create and Review Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is a fundamental network security and cybersecurity compliance requirement. With Palo Alto firewalls, you should consider the following best practices, at a minimum:
- Create zones to control traffic flowing through firewall interfaces
- Build Zone Protection profiles to mitigate Denial of Service (DoS) attack risks
- Set Security Policy rules for between and within zones
- Create policy rules
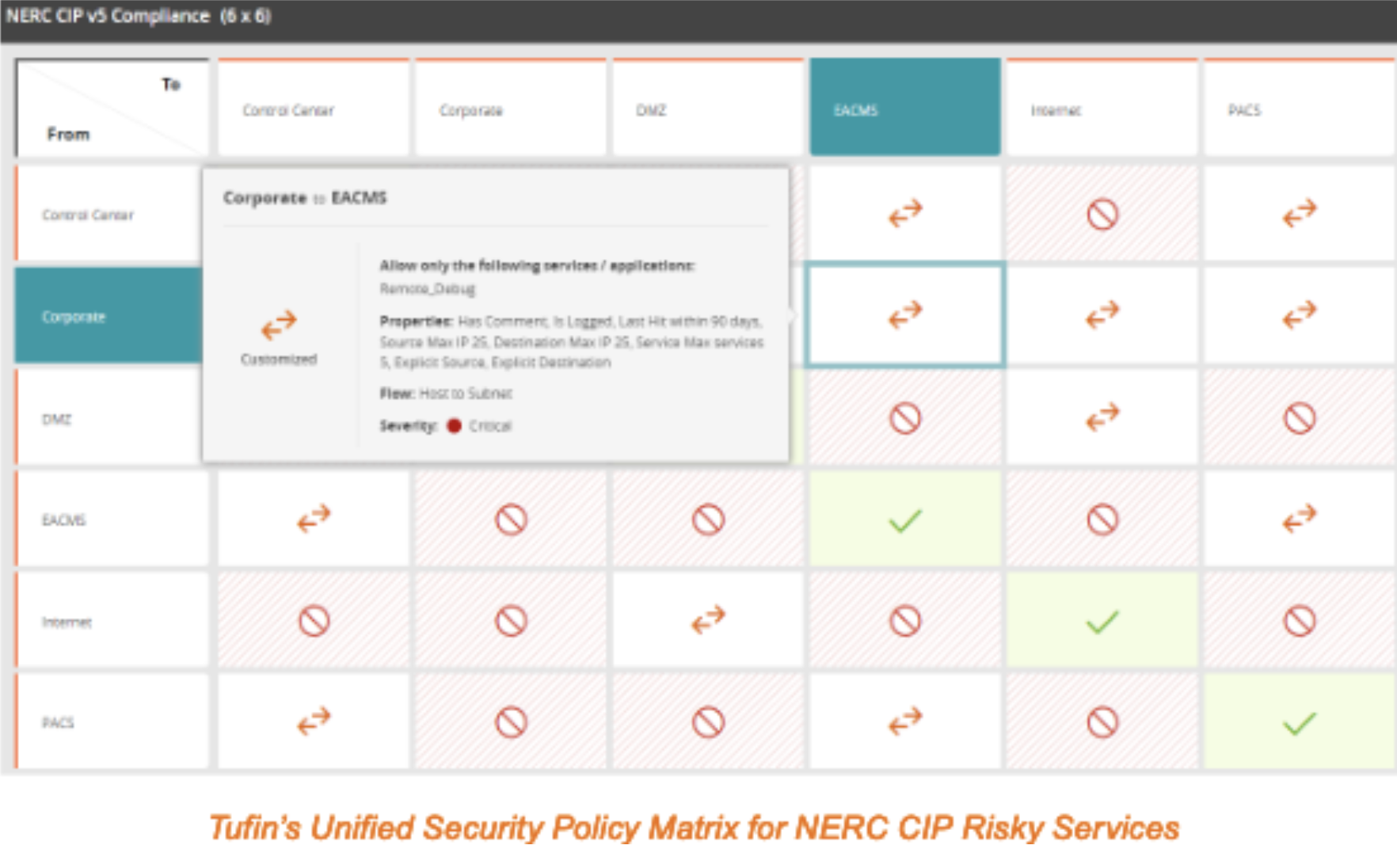
Segmenting your networks can become challenging, especially when you need to achieve specific compliance objectives. For example, you might need to comply with both PCI DSS to protect payment card information and HIPAA to protect health information. You might understand how these different – and sometimes overlapping – data types flow across your networks but managing them can feel overwhelming. With Tufin, you create visualizations showing:
- Network access across vendors and devices
- Services permitted on network segments
- Access polices that violate the compliance model
- Exceptions to policies for tracking recertifications
Establish Security Policy Rules
Security policy rules tell the firewall how to take action on traffic. Ordering them logically in the rulebase helps you manage security more effectively. Some considerations include:
- Placing rules blocking malicious traffic at the top of the rulebase
- Allowing basic applications and common services near the top of the rulebase to prevent accidentally blocking them
- Placing specific rules near the top of the rulebase
- Placing general rules toward the bottom of the rulebase to prevent them from shadowing a rule
- Using application and address groups
- Disabling or removing rules from the Security policy rulebase when no longer necessary
While writing the initial Security policy rulebase may seem intuitive, maintaining them becomes overwhelming as you grow your environment and add more firewall vendors. With Tufin, you can reduce the amount of time spent on network management with functionalities to help manage Panorama (PanOS), including:
- Summaries of disabled, fully shadowed, or low-usage rules
- Rules with violations
- Automatic Policy Generation (APG) that analyzes firewall logs to understand business practices and optimize the rulebase
Understand Users and Application Usage
Palo Alto firewalls allow you to create rules for user network and application access. Some considerations might include:
- Identifying applications necessary for business purposes
- Identifying applications that people use for identifying applications without an associated purpose
- Specifying Security policy rules that allow access
- Specifying Security policy rules that deny, drop, or reset traffic
- Identifying all users and requiring authentication prior to granting access to applications
- Identifying all devices and requiring authentication prior to granting access to resources
- Creating consistent policies for users across the entire network
When you use Palo Alto firewalls as part network management, you may find that aligning their proprietary rule terminology with security policy terms for other vendors. For example, Palo Alto firewall rules use proprietary terms like:
- User-ID: term to identify users by more than just IP address
- App-ID: proprietary classification to determine application my mapping traffic to SSL or SSH being used and Decryption policy rule
Tufin’s Universal Security Policies (USP) take the heavy lifting off your shoulders by creating vendor-agnostic rules that allow you to get the most from your Palo Alto firewalls while integrating them into a larger network infrastructure.
Maintain Secure Firewall Configurations
While getting your firewalls installed is the first step, maintaining secure, compliance configurations is the long game. When monitoring your Palo Alto firewall deployment, you should consider:
- Tracking applications, users, and devices added to or deleted from your environment
- Running regular network security posture analyses
- Reviewing policy rules when adding new applications to your network
- Deleting applications from policy rules promptly to protect against unauthorized access
- Conducting a risk analysis before implementing new security policies
Incorporate Firewall Data into Security Operations
Palo Alto Networks offers DoS protection to help you manage cybersecurity risk more effectively. Some key considerations when integrating your firewalls into your security operations include:
- Forwarding Palo Alto firewall logs to your security information and event management (SIEM) tool
- Setting notifications related to DoS attack indicators
- Understanding network traffic patterns to identify anomalies
Tufin: Centralizing Visibility and Network Security Management
Tufin’s easy-to-use management interface allows you to manage hybrid networks and improve network security. Tufin’s topology maps show you traffic flows across your internal networks and public facing resources for visibility into security and service availability.
Our change management workflows automate the risk analysis process, improving efficiency by 94%. By using our USPs, you can ensure consistent user, device, and application access across a complex environment consisting of various firewall vendors, including Cisco, Palo Alto, Check Point, and Fortinet.
To see how Tufin can make managing your hybrid network easier, contact us for a demo.
FAQs
Q: What are the Palo Alto Networks CIS Benchmarks
A: The Palo Alto Networks CIS Benchmarks set out secure configuration guidelines developed from a community consensus process. They can be used to map to other mission critical compliance mandates, like
- NIST 800-53
- PCI DSS
- HIPAA
- NERC CIP
- ISO 27001
Q: What are some key Palo Alto Firewall features?
A: You can choose various Palo Alto firewall features using a subscription method. Some key security services include:
- SD-WAN: intelligent and dynamic path selection managed through Panorama
- Threat prevention: Antivirus, anti-spyware, vulnerability protection, infected host detection, dynamic lists, and WildFire for signature updates
- DNS Security: sinkholing and DNS signature generation with access to Palo Alto Networks DNS-based threat intelligence
- URL Filtering: dynamic URL categories to control web access and user interaction with online content using
- GlobalProtect Gateway: remote access security with large-scale VPN capabilities
- SaaS Security Inline: SaaS application and shadow IT discovery, SaaS policy rule recommendations and enforcement
Ready to Learn More
Get a Demo